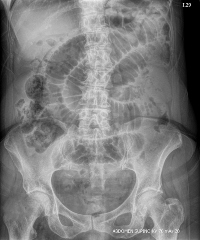
Radiografía simple de abdomen: una mirada a la patología abdominal a partir del patrón gaseoso
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53903/01212095.201Resumen
La radiografía de abdomen simple es una herramienta disponible en casi cualquier institución de salud. Los profesionales médicos tienen dificultades en su interpretación, lo cual, además de sus limitaciones inherentes, pone en duda la utilidad de este método de imagen. Dado que su principal indicación de urgencia es el dolor abdominal con sospecha en obstrucción intestinal, es imperativo abordar su análisis de forma ordenada, poniendo en práctica los conocimientos previos de la anatomía abdominal, los requisitos técnicos para la adecuada adquisición de la imagen, el análisis del patrón gaseoso intraabdominal, los órganos sólidos, las calcificaciones, los cuerpos extraños y los dispositivos médicos.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Eastman Kodak Company staff. Elementos de radiografía. Eastman Kodak; 1980.
Scheirey C, Fowler C, Therrien J, Kim D, Al-Refaie W, CamachoM, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria® 1 acute nonlocalized abdominal pain American college of radiology [Internet]. S. f. [citado: 2022 ene 27]. Disponible en: https://acsearch.acr.org/docs/69467/Narrative/
Ahn SH, Mayo-Smith WW, Murphy BL, Reinert SE, Cronan JJ. Acute nontraumatic abdominal pain in adult patients: abdominal radiography compared with CT evaluation. Radiology. 2002;225(1):159-64. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2251011282
Pandharipande PV, Reisner AT, Binder WD, Zaheer A, Gunn ML, Linnau KF, et al. CT in the emergency department: A real-time study of changes in physician decision making. Radiology. 2016;278(3):812-21. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015150473
MacKersie AB, Lane MJ, Gerhardt RT, Claypool HA, Keenan S, Katz DS & Tucker JE. Nontraumatic acute abdominal pain: unenhanced helical CT compared with threeview acute abdominal series. Radiology. 2005;237(1):114-22. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2371040066.
Eisenberg RL, Heineken P, Hedgcock MW, Federle M, Goldberg HI. Evaluation of plain abdominal radiographs in the diagnosis of abdominal pain. Ann Surg. 1983;197(4):464-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00000658-198304000-00016
Aras MH, Miloglu O, Barutcugil C, Kantarci M, Ozcan E, Harorli A. Comparison of the sensitivity for detecting foreign bodies among conventional plain radiography, computed tomography and ultrasonography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2010;39(2):72-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1259/dmfr/68589458
Hunter TB, Taljanovic MS. Medical devices of the abdomen and pelvis. Radiographics. 2005;25(2):503-23. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/rg.252045157
Coursey CA, Casalino DD, Remer EM, Arellano RS, Bishoff JT, Dighe M, et al. ACR appropriateness criteria® acute onset flank pain–suspicion of stone disease. Ultrasound Q. 2012;28(3):227-33. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/ruq.0b013e3182625974
Bontrager KL, Lampignano J. Textbook of radiographic positioning and related anatomy. 8a ed. Londres, Inglaterra: Mosby; 2014.
Laufer I. The left lateral view in the plain-film assessment of abdominal distension. Radiology. 1976;119(2):265-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/119.2.265
Gore RM, Levine MS. Textobook of gastrointestinal radiology Vol 2. Elsevier; 2015.
Whalen JP, Berne AS, Riemenschneider PA. The extraperitoneal perivisceral fat pad. I. Its role in the roentgenologic visualization of abdominal organs: I. Its role in the roentgenologic visualization of abdominal organs. Radiology. 1969;92(3):466-72. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/92.3.466
Loo JT, Duddalwar V, Chen FK, Tejura T, Lekht I, Gulati M. Abdominal radiograph pearls and pitfalls for the emergency department radiologist: a pictorial review. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017;42(4):987-1019. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-0859-8
Nair N, Takieddine Z, Tariq H. Colonic interposition between the liver and right diaphragm: The “Chilaiditi sign”. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. v.2016;2016. PMC4904707.
Thompson WM. Gasless abdomen in the adult: What does it mean? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191(4):1093-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.2214/ajr.07.3837
Seaman WB. Motor dysfunction of the gastro-intestinal tract. Am J Roentgenol Rad Ther Nucl Med. 1972;116(2):235-44.
Böhm B, Milsom JW, Fazio VW. Postoperative intestinal motility following conventional and laparoscopic intestinal surgery. Arch Surg. 1995;130(4):415-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1001/archsurg.1995.01430040077017
Kammen BF, Levine MS, Rubesin SE, Laufer I. Adynamic ileus after caesarean section mimicking intestinal obstruction: findings on abdominal radiographs. Br J Radiol. 2000;73(873):951-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.1259/bjr.73.873.11064647
Musson RE, Bickle I, Vijay RKP. Gas patterns on plain abdominal radiographs: a pictorial review. Postgrad Med J. 2011;87(1026):274-87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/pgmj.2009.082396
Ali N, Leshchinskiy S, Johnson M, D’Agostino R. The sentinel loop sign. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2018;43(11):3192-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1582-4
Davis S, Parbhoo SP, Gibson MJ. The plain abdominal radiograph in acute pancreatitis. Clin Radiol. 1980;31(1):87-93. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0009-9260(80)80088-2
Silva AC, Pimenta M, Guimarães LS. Small bowel obstruction: what to look for. Radiographics. 2009;29(2):423-39. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/rg.292085514
Harlow CL, Stears RL, Zeligman BE, Archer PG. Diagnosis of bowel obstruction on plain abdominal radiographs: significance of air-fluid levels at different heights in the same loop of bowel. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1993;161(2):291-5. http://dx.doi.org/10.2214/ajr.161.2.8333364
Burgess LK, Lee JT, DiSantis DJ. The String of pearls sign. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016;41(7):1435-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-0683-1
Hayakawa K, Tanikake M, Yoshida S, Urata Y, Yamamoto E, Morimoto T. Radiological diagnosis of large-bowel obstruction: neoplastic etiology. Emerg Radiol.2013;20(1):69-76. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10140-012-1088-2
Jaffe T, Thompson WM. Large-bowel obstruction in the adult: Classic radiographic and CT findings, etiology, and mimics. Radiology. 2015;275(3):651-63. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015140916
Hussain ZH, Whitehead DA, Lacy BE. Fecal impaction. Curr Gastroenterol Rep.2014;16(9). http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11894-014-0404-2
Saksonov M, Bachar GN, Morgenstern S, Zeina A-R, Vasserman M, Protnoy O, et al. Stercoral colitis: a lethal disease-computed tomographic findings and clinical characteristic. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2014;38(5):721-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/RCT.0000000000000117
Burrell HC, Baker DM, Wardrop P, Evans AJ. Significant plain film findings in sigmoid volvulus. Clin Radiol. 1994;49(5):317-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s0009-9260(05)81795-7
Javors BR, Baker SR, Miller JA. The northern exposure sign: A newly described finding insigmoid volvulus. AJR. 1999;173:571-4.
Lassandro G, Picchi SG, Romano F, Sica G, Lieto R, Bocchini G, et al. Intestinal pneumatosis: differential diagnosis. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02639-8.
Feczko PJ, Mezwa DG, Farah MC, White BD. Clinical significance of pneumatosis of the bowel wall. Radiographics. 1992;12(6):1069-78. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiographics.12.6.1439012
Soyer P, Martin-Grivaud S, Boudiaf M, et al. Linear or bubbly: a pictorial review of CT features of intestinal pneumatosis in adults. J Radiol. 2008;89(12):1907-20.
Indiran V, Sivakumar V. Rigler sign. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017;42(10):2588. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1149-9
Indiran V, Maduraimuthu P. Falciform ligament sign. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017;42(4):1287-8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-0995-1
Marshall GB. The cupola sign. Radiology. 2006;241(2):623-4. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2412040700
Lin AC, Wu CC, Su CT. Classic signs of pneumoperitoneum on supine abdominal radiograph. Am J Emerg Med. 2006;24(5):642-3. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2005.12.023-Pubmedcitation
Sherman SC, Tran H. Pneumobilia: benign or life-threatening. Emerg Med. 2006;30:147-53.
Gosink BB. Intrahepatic gas: differential diagnosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1981;137(4):763-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.2214/ajr.137.4.763
Chang L, Chang M, Chang HM, Chang AI, Chang F. Clinical and radiological diagnosis of gallstone ileus: a mini review. Emerg Radiol. 2018;25(2):189-96. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10140-017-1568-5
Han SY, Tishler JM, Aldrete JS. Extraperitoneal gas: compartmental localization and identification of source. J Can Assoc Radiol. 1985;36(1):17-21.
Yacoub JH, Clark JA, Paal EE, Manning MA. Approach to cystic lesions in the abdomen and pelvis, with radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2021;41(5):1368-86. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2021200207
Gelfand DW. The liver: Plain film diagnosis. Semin Roentgenol. 1975;10(3):177-85. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/0037-198x(75)90060-7
Sirakov V, Sirakova A, Izmirlieva S. New indirect X-ray symptoms of discrete hepatomegaly. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 1991;33(4):32-5.
Gunes SO, Akturk Y. Determination of splenomegaly by coronal oblique length on CT. Jpn J Radiol. 2018;36(2):142-50. http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s11604-017-0704-1
Bundrick TJ, Cho SR, Brewer WH, Beachley MC. Ascites: comparison of plain film radiographs with ultrasonograms. Radiology. 1984;152(2):503-6. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/radiology.152.2.6739823
Wixson D, Kazam E, Whalen JP. Displaced lateral surface of the liver (Hellmer’s sign) secondary to an extraperitoneal fluid collection. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1976;127(4):679-82. http://dx.doi.org/10.2214/ajr.127.4.679
Love L, Demos TC, Reynes CJ, Williams V, Shkolnik A, Gandhi V, et al. Visualization of the lateral edge of the liver in ascites. Radiology. 1977;122(3):619-22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/122.3.619
Zulfiqar M, Shetty A, Tsai R, Gagnon M-H, Balfe DM, Mellnick VM. Diagnostic approach to benign and malignant calcifications in the abdomen and pelvis. Radiographics. 2020;40(3):731-53. http://dx.doi.org/10.1148/rg.2020190152
Brown RC, Loening SA, Ehrhardt JC, Hawtrey CE. Cystine calculi are radiopaque. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1980;135(3):565-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.2214/ajr.135.3.565
Fulgham PF, Assimos DG, Pearle MS, Preminger GM. Clinical effectiveness protocols for imaging in the management of ureteral calculous disease: AUA technology assessment. J Urol. 2013;189(4):1203-13. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2012.10.031
Jones MW, Kashyap S, Ferguson T. Gallbladder Imaging. StatPearls Publishing; 2021
Kamat R, Gupta P, Rana S. Imaging in chronic pancreatitis: State of the art review. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2019;29(02):201-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.4103/ijri.ijri_484_18
Mathew RP, Department of Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging, University of Alberta School of Medicine and Dentistry, Edmonton, Canada, Sam M, Alexander T, Patel V, Low G, et al. Abdominal and pelvic radiographs of medical devices and materials—Part 1: gastrointestinal and vascular devices and materials. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2020;26(2):101-10. http://dx.doi.org/10.5152/dir.2019.19390
Mathew RP, Department of Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging, University of Alberta School of Medicine and Dentistry, Edmonton, Canada, Sam M, Alexander T, Patel V, Low G, et al. Abdominal and pelvic radiographs of medical devices and materialspart 2: neurologic and genitourinary devices and materials. Diagn Interv Radiol.2020;26(3):160-7. http://dx.doi.org/10.5152/dir.2019.19391.
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2023 Revista colombiana de radiología

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
La Revista Colombiana de Radiología es de acceso abierto y todos sus artículos se encuentran libre y completamente disponibles en línea para todo público sin costo alguno.
Los derechos patrimoniales de autor de los textos y de las imágenes del artículo como han sido transferidos pertenecen a la Asociación Colombiana de Radiología (ACR). Por tanto para su reproducción es necesario solicitar permisos y se debe hacer referencia al artículo de la Revista Colombiana de Radiología en las presentaciones o artículos nuevos donde se incluyan.