Enfermedad de Rosai-Dorfman (ERD) con compromiso exclusivo del sistema nervioso central. Presentación de caso y revisión de literatura
Palabras clave:
Histiocitosis sinusal, Sistema nervioso central, Tomografía computarizada por rayos XResumen
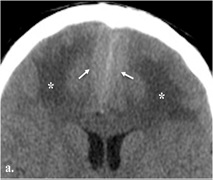
La enfermedad de Rosai-Dorfman (ERD) o histiocitosis sinusal con linfadenopatía masiva (HSLM) es una entidad histiocítica benigna rara, que usualmente afecta los ganglios linfáticos. Se han descrito algunos casos en el sistema nervioso central, y son excepcionales los que aparecen sin afección nodular concomitante. La falta de patrones imaginológicos cerebrales típicos puede llevar a una cirugía por un diagnóstico erróneo, con causas atribuidas a un probable origen maligno. Usualmente, el diagnóstico histopatológico se realiza después del procedimiento quirúrgico. Esta entidad clínico-patológica carece de consenso en diagnóstico, curso clínico y tratamiento. Se presenta un caso de ERD con extensión intracraneal, con la lectura retrospectiva de los estudios imaginológicos.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Rosai J, Dorfman RF. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy. A newly recognized benign clinicopathological entity. Arch Pathol. 1969;87(1):63-70.
Xu Q, Fu L, Liu C. Multimodality imaging-based evaluation of Rosai–Dorfman disease in the head and neck. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(51): e9372.
Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman R. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai- Dorfman disease): review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990;7(1):19-73.
Yang K, Kolakshyapati M, Shrestha T, Lou L. Isolated intramedullary Rosai–Dorfman disease. Surg Neurol Int [internet]. 2016 [citado 2018 mar. 16];7. Disponible en: https:// www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5223399/.
Alimli AG, Oztunali C, Boyunaga OL, Pamukcuoglu S, Okur A, Borcek AO. MRI and CT findings of isolated intracranial Rosai–Dorfman disease in a child. Neuroradiol J. 2016;29(2):146-9.
Andriko J-AW, Morrison A, Colegial CH, Davis BJ, Jones RV. Rosai-Dorfman disease isolated to the central nervous system: A Report of 11 Cases. Mod Pathol. 2001;14(3):172-8.
Krishnamoorthy V, Parmar C, Panikar D. Isolated intracranial Rosai Dorfman disease. Neurol India. 2011;59:443-6.
Li Y, Sun H, Zhang Y, Liu W. Isolated intracranial Rosai–Dorfman disease presenting as mental deterioration. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2012;114(7):1070-3.
Foss H-D, Herbst H, Araujo I, Hummel M, Berg E, Schmitt-Gräff A, et al. Monokine. Expression in Langerhans’ Cell histiocytosis and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (rosai–Dorfman Disease). J Pathol. 1996;179(1):60-5.
Levine PH, Jahan N, Murari P, Manak M, Jaffe ES. Detection of human herpesvirus 6 in tissues involved by sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease). J Infect Dis. 1992;166(2):291-5.
Mehraein Y, Wagner M, Remberger K, Füzesi L, Middel P, Kaptur S, et al. Parvovirus B19 detected in Rosai-Dorfman disease in nodal and extranodal manifestations. J Clin Pathol. 2006;59(12):1320-6.
Paulli M, Bergamaschi G, Tonon L, Viglio A, Rosso R, Facchetti F, et al. Evidence for a polyclonal nature of the cell infiltrate in sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease). Br J Haematol. 1995;91(2):415-8.
Fukushima T, Yachi K, Ogino A, Ohta T, Watanabe T, Yoshino A, et al. Isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease without dural attachment. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2011;51(2):136-40.
Di R, Garnett MR, Puget S, Pueyerredon F, Roujeau T, Jaubert F, et al. Cerebral localization of Rosai-Dorfman disease in a child: Case report. J Neurosurg. 2007;107(2 suppl.):147-51.
Natarajan S, Post KD, Strauchen J, Morgello S. Primary intracerebral rosai-dorfman disease: a case report. J Neurooncol. 2000;47(1):73-7.
Gaetani P, Tancioni F, Di Rocco M, Rodríguez y Baena R. Isolated cerebellar involvement in Rosai-Dorfman disease: case report. Neurosurgery. 2000;46(2):479-81.
Triana-Pérez AB, Sánchez-Medina Y, Pérez-Del Rosario PA, Millán-Corada AM, Gómez-Perals LF, Domínguez-Báez JJ. [Isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease: a case report and literature review]. Neurocir Astur Spain. 2011;22(3):255-60.
Sandoval-Sus JD, Sandoval-León AC, Chapman JR, Velázquez-Vega J, Borja MJ, Rosenberg S, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease of the central nervous system: Report of 6 cases and review of the literature. medicine (Baltimore). 2014;93(3):165-75.
Forest F, N’Guyen AT, Fesselet J, Metellus P, Bouvier C, Paula AM de, et al. Meningeal Rosai–Dorfman disease mimicking meningioma. Ann Hematol. 2014;93(6):937-40.
Huang BY, Zong M, Zong WJ, Sun YH, Zhang H, Zhang HB. Intracranial Rosai– Dorfman disease. J Clin Neurosci. 2016;32:133-6.
Griffiths SJ, Tang W, Parameswaran R, Kelsey A, West CGH. Isolated intracranial Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking meningioma in a child. Br J Neurosurg. 2004;18(3):293-7.
Cooper SL, Jenrette JM. Rosai-Dorfman Disease: Management of CNS and systemic involvement. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2012;10(3):199-202.
Kumar KK, Menon G, Nair S, Radhakrishnan VV. Rosai-Dorfman disease mimicking chronic subdural hematoma. J Clin Neurosci. 2008;15(11):1293-5.
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
La Revista Colombiana de Radiología es de acceso abierto y todos sus artículos se encuentran libre y completamente disponibles en línea para todo público sin costo alguno.
Los derechos patrimoniales de autor de los textos y de las imágenes del artículo como han sido transferidos pertenecen a la Asociación Colombiana de Radiología (ACR). Por tanto para su reproducción es necesario solicitar permisos y se debe hacer referencia al artículo de la Revista Colombiana de Radiología en las presentaciones o artículos nuevos donde se incluyan.