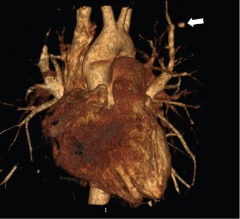
Rasmussen´s Pseudoaneurysm: A Rare But an Important Cause of Hemoptysis. A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53903/01212095.37Keywords:
Hemoptysis, Aneurysm, Tuberculosis, Pulmonary artery, RadiologyAbstract
Rasmussen’s pseudoaneurysm is one of the causes of hemoptysis that, despite not being very common, is important to recognize and take into account in the approach of these patients. It typically occurs in the context of massive hemoptysis and its approach in addition to patient stabilization is focused on recognizing it as a differential diagnosis. The initial approach for these patients includes conventional chest radiography; however, computed tomography (CT) and CT[1]angiography have shown the highest diagnostic performance. For its treatment, transcatheter arterial embolization has established itself as the technique of choice; however, in some cases open surgical management may be necessary
Downloads
References
Bruzzi JF, et al. Multi-detector row CT of hemoptysis. Radiographics. 2006;26:3-22.
Rajamannar KV, Kilaru H, Aravelly S, Gudipati AR, Kilaru SC. Massive hemoptysis from Rasmussen’s aneurysm in active pulmonary tuberculosis; A case report of successful treatment with bronchial artery embolization. Respir. Med. Case Reports. 2017;22:277-9.
Kim HY, et al. Thoracic sequelae and complications of tuberculosis. RadioGraphics. 2001;21:839-58.
Jones R, Charlton J, Latinovic R, Gulliford MC. Alarm symptoms and identification of non-cancer diagnoses in primary care: Cohort study. BMJ. 2009;339:491-3.
Abdulmalak C, et al. Haemoptysis in adults: A 5-year study using the French nationwide hospital administrative database. Eur. Respir. J. 2015;46:503-11.
Fartoukh M, et al. An integrated approach to diagnosis and management of severe haemoptysis in patients admitted to the intensive care unit: A case series from a referral centre. Respir. Res. 2007;8:1-9.
Olsen KM, et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Hemoptysis. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2020;17:S148-59.
Tom LM, et al. Recurrent bleeding, survival, and longitudinal pulmonary function following bronchial artery embolization for hemoptysis in a U.S. adult population. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2015;26:1806-13.e1.
Panda A, Bhalla AS, Goyal A. Bronchial artery embolization in hemoptysis: A syste matic review. Diagnostic Interv. Radiol. 2017;23:307-17.
Sakr L, Dutau H. Massive hemoptysis: An update on the role of bronchoscopy in diagnosis and management. Respiration. 2010;80:38-58.
Uzun O, Atasoy Y, Findik S, Atici AG, Erkan L. A prospective evaluation of hemoptysis cases in a tertiary referral hospital. Clin. Respir. J. 2010;4:131-8.
Kervancioglu S, Bayram N, Yilmaz FG, Sanli M, Sirikci A. Radiological findings and outcomes of bronchial artery embolization in cryptogenic hemoptysis. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015;30:591-7.
Peghini Gavilanes E, Fernández-Velilla M, Bermejo Moriñigo A, Morales Ruiz R Pseudoaneurisma de Rasmussen: hallazgos en tomografía computada. Revisión de casos. Rev. Argentina Radiol. 2016;80:122-6.
Instituto Nacional de Salud. Una mirada hacia el comportamiento de la tuberculosis en Colombia, 2018 (Semanas epidemiológicas 1-36). 35 (2018).
Shih SY, Tsai IC, Chang YT, Tsan YT, Hu SY. Fatal haemoptysis caused by a ruptured Rasmussen’s aneurysm. Thorax. 2011;66:553-4.
Neelakantan S, Anandarajan R, Swamy AK. Rare cause of massive haemoptysis in pulmonary tuberculosis: Rasmussen’s aneurysm. BMJ Case Rep. 2016;3-5.
Ossés JM. ¿Qué sabemos de los aneurismas de la arteria pulmonar? Rev. Am. Med. Respir. 2014;14:92-3.
Vicente Antunes SI, Rodríguez Martín P, de San Pablo Sánchez AM. Hemoptisis. Cirugía en Patología Pulmonar no tumoral. 2010;XVI:147-59.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
La Revista Colombiana de Radiología es de acceso abierto y todos sus artículos se encuentran libre y completamente disponibles en línea para todo público sin costo alguno.
Los derechos patrimoniales de autor de los textos y de las imágenes del artículo como han sido transferidos pertenecen a la Asociación Colombiana de Radiología (ACR). Por tanto para su reproducción es necesario solicitar permisos y se debe hacer referencia al artículo de la Revista Colombiana de Radiología en las presentaciones o artículos nuevos donde se incluyan.