Ultrasound Evaluation of the Muscular Structural Parameters in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.53903/01212095.78Keywords:
Ultrasonography, Musculoskeletal system, Lupus erythematosus systemic, MyositisAbstract
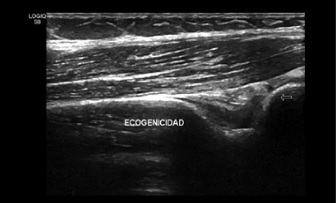
Objective: To detect muscle structure alterations related to patients diagnosed with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and to describe their relationship with disease activity and time of treatment. Methods: patients > 18 years with diagnosis of SLE affiliated to Sanitas Health System and treated during the period from January 2016 to September 2018. The demographic, clinical and serological information were obtained from the patient’s medical records, prior to ultrasound examination from the proximal pennate triceps and vastus lateralis muscles. The qualitative and quantitative variables of the muscular architecture were evaluated (muscle thickness, fascicle length, angle of pennation, echogenicity, atrophy and muscular edema). Results: 21 patients were included of which 18 were women (85.7%), 19 of them in the age range of 18-50 years (90.4%), 15 patients reported myalgia in the interview (71%) and 7 presented loss of their strength in the MRC scale (33%). The majority of patients received a steroid-based treatment (95%) plus a disease-modifying medication. Ten patients presented a mild to moderate disease activity index (81.2%). Regarding ultrasound measurements, we found a relationship between a pennation angle of less than 11.4 degrees and the presence of atrophy with a value of p = 0.035. Conclusions: Musculoskeletal ultrasound is a useful non-invasive method for detecting changes in the muscle architecture of the vastus lateralis muscle in patients diagnosed with SLE.
Downloads
References
Cojocaru M, Cojocaru IM, Silosi I, Vrabie CD. Manifestations of systemic lupus erythematosus. Mædica. 2011;6(4):330-6.
Zoma A. Musculoskeletal involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2004;13(11):851-3.
Delle Sedie A, Riente L, Scirè CA, Iagnocco A, Filippucci E, Meenagh G, et al. Ultrasound imaging for the rheumatologist XXIV. Sonographic evaluation of wrist and hand joint and tendon involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2009;27(6):897-901.
Wallace DJ. The musculoskeletal system. 5th edition. Wallace DJ HB, editor. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins; 1997. 635-51 p.
Connell MJO, Powell T, Brennan D, Lynch T, Eustace SJ. Original report whole-body MR imaging in the diagnosis of polymyositis. 2002;179(October):967-71.
Ayala AP, Escobar RE, Espinosa R, et al. Estudios de imagen y electromiografía en las miopatías inflamatorias. Reumatol Clin. 2009;5(S3):23-7.
Reimers CD, Fleckenstein JL, Witt TN. Muscular ultrasound in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies of adults. J Neurol Sci. 1993;116(1993):82-92.
Kaya A, Kara M, Tiftik T, et al. Ultrasonographic evaluation of the muscle architecture in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 2013;32:1155-60.
Gladman D, Ibáñez D, Urowitz M. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000. J Rheumatol. 2002;29:2.
Hochberg MC. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40(9):1725.
Aids to the investigation of peripheral nerve injuries. Medical Research Council: Nerve Injuries Research Committee. His Majesty’s Stationery Office: 1942; pp. 48 (iii) and 74 figures and 7 diagrams.
EULAR Ultrasound Scanning Guide. http://ultrasound.eular.org/#/home.
Heckmatt JZ, Leeman S, Dubowitz V. Ultrasound imaging in the diagnosis of muscle disease. J Pediatr. 1982;101(5):656-60.
http://zeus.colsanitas.com/manual_referencia/parametros_referencia.php.
Bosch X, Formiga F, López-Soto A. Lupus eritematoso sistémico en el anciano. Rev Esp Geriatr Gerontol. 2012;10:1016.
Paredes N, Torres E, Montiel-Jarolin D. Lupus eritematoso sistémico de inicio tardío. Publicación Oficial del Hospital Nacional. 2012.
Alonso MD, Martínez-Vásquez F, Díaz de Terán T, et al. Late-onset systemic lupus erythematosus in Northwestern Spain: differences with early-onset systemic lupus erythematosus and literature review. Lupus. 2012;21:1135-48.
Jakati S, Rajasekhar L, Uppin M. SLE myopathy: a clinicopathological study. Int J Rheumatic Dis. 2015;18:886-89.
Maazoun F, Frikha F, Snoussi M, Kaddour N, Masmoudi H, Bahloul Z. Systemic lupus erythematosus myositis overlap syndrome: report of 6 cases. Clin Pract. 2011;194:e89.
Isenberg DA, Snaith ML, Morrow WJ, et al. Cyclosporine A for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1981;3:163-9.
Tsokos GC, Moutsopoulos HM, Steinberg AD. Muscle involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus. JAMA. 1981;246(5):766-8.
Kwah LK, Pinto RZ, Diong J, et al. Reliability and validity of ultrasound measure-ments of muscle fascicle length and pennation in humans: a systematic review. J Appl Physiol. 2013;114:761-9.
Rutherford OM, Jones DA. Measurement of fibre pennation using ultrasound in the human quadriceps in vivo. Eur J Appl Physiol. 1992;65:433-7.
Fukunaga T, Ichinose Y, Ito M, et al. Determination of fascicle length and pennation in a contracting human muscle in vivo. J Appl Physiol. 1997;82(1):354-8.
Blazevich AJ, Cannavan D, Coleman DR. Influence of concentric and eccentric resistance training on architectural adaptation in human quadriceps muscles. J Appl Physiol. 2007;103:1565-75.
Matzumura JP, Gutiérrez H, Sotomayor J. Evaluación de la calidad de registro de historias clínicas en consultorios externos del servicio de medicina interna de la Clínica Centenario Peruano Japonesa, 2010-2011. An Fac med. 2014;75(3):251-7.
Adeleke TI, Adekanye AO, Onawola KA, et al. Data quality assessment in healthcare: a 365-day chart review of inpatients’ health records at a Nigerian tertiary hospital. J Am Med Informatics Association. 2012;19(6):1039-42.
Gupta A, Gupta Y. Glucocorticoid-induced myopathy: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Indian J Endocrinol Metabolism. 2013;17:913-16.
Minneto MA, D’Angelo V, Arvat E, Kesari S. Diagnostic work-up in steroid myopathy. Endocrine. 2018;60(2):219-23.
Tselios K, Gladman DD, Su J, Urowitz MB. Antimalarials as a risk factor for elevated muscle enzymes in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2016;25(5):532-5.
Zhou Y, Zheng Y-P. Estimation of muscle fiber orientation in ultrasound images using Revoting Hough Transform (RVHT). Ultrasound Med. Biol., 2008;34(9):1474-81.
Zhou G-Q, Chan P, Zheng Y-P. Automatic measurement of pennation angle and fascicle length of gastrocnemius muscles using real-time ultrasound imaging. Ultrasonics. 2015;57:72-83.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
La Revista Colombiana de Radiología es de acceso abierto y todos sus artículos se encuentran libre y completamente disponibles en línea para todo público sin costo alguno.
Los derechos patrimoniales de autor de los textos y de las imágenes del artículo como han sido transferidos pertenecen a la Asociación Colombiana de Radiología (ACR). Por tanto para su reproducción es necesario solicitar permisos y se debe hacer referencia al artículo de la Revista Colombiana de Radiología en las presentaciones o artículos nuevos donde se incluyan.